Ransomware is a sort of malware assault that encrypts files on a system, rendering the victim unavailable. The attacker then demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key, which will allow the files to be unlocked and decrypted.
Typically, ransomware attacks target flaws in human behavior, system setups, network infrastructure, or software applications. Phishing emails, malware downloads and drive-by downloads are all prevalent methods of delivery.
When a device is infected with ransomware, the attack proceeds in stages. The ransomware is first secretly downloaded and installed on the device. Then it scans and maps the device for specific file types before encrypting them with an encryption key controlled by the attacker. A ransom letter is presented, usually demanding bitcoin payment. There is no guarantee that the victim will receive the decryption key if they pay the ransom.
There are different forms of ransomware, each with its own set of characteristics and means of dissemination. WannaCry, Cerber, Locky, Cryptolocker, NotPetya, Ryuk, and GrandCrab are some well-known instances.
Several recommended practices can be implemented by enterprises to protect themselves from ransomware attacks. Using next-generation antivirus solutions, regularly backing up data offline, patching and updating software and operating systems, employing application whitelisting and control, conducting cybersecurity awareness training, and implementing network defenses such as firewalls and web application firewalls are all examples.
When a ransomware attack is active, it is critical to isolate the infected workstations, analyze possible backups, and assess whether paying the ransom is a viable alternative. Following that, compromised systems should be cleansed and reinstalled, vulnerabilities repaired, and the attack’s lessons learnt.
Follow these precautions to avoid ransomware attacks:
1. Maintain software updates: Update your operating system, antivirus software, and other apps on a regular basis. Security patches that can protect against vulnerabilities by ransomware are frequently included in updates.
2. Use strong, unique passwords: Avoid using readily guessable passwords and instead consider using a password manager to generate and store secure, unique passwords for each of your accounts.
3. Email attachments and links should be avoided: Do not open attachments or click on links in emails from unknown senders or suspect sources. These are potential vectors for ransomware infestations. Be especially vigilant of communications that appear urgent or request personal information.
4. Backup your data on a regular basis: Back up your vital data on a regular basis to an external hard drive, cloud storage, or a dedicated backup service. This assures that even if your files are encrypted by ransomware, you will be able to restore them without having to pay the ransom.
5. Enable automated backups and restore points: Set your computer to produce backups or restore points at regular intervals. This can assist you in recovering your files in the event of a ransomware attack.
6. Use reliable antivirus software: Install and keep up to date reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on all of your devices. These programs can aid in the detection and prevention of ransomware infections.
7. Educate yourself and your employees: Inform yourself and your staff on the dangers of ransomware and how to spot and avoid possible threats. Teach kids about safe web browsing, phishing scams, and how to spot strange emails or websites.
8. Allow popups and disable macros: Allow popups in your web browser and disable macros in Office documents. These can assist in preventing malicious scripts or macros from running and infecting your device with ransomware.
9. Use a firewall: Install and maintain a firewall on your network to filter out potential risks and limit unwanted access to your devices.
10. When downloading files or applications, use caution: Download files and software only from trusted sources. Avoid downloading files from unknown websites or dubious sources.
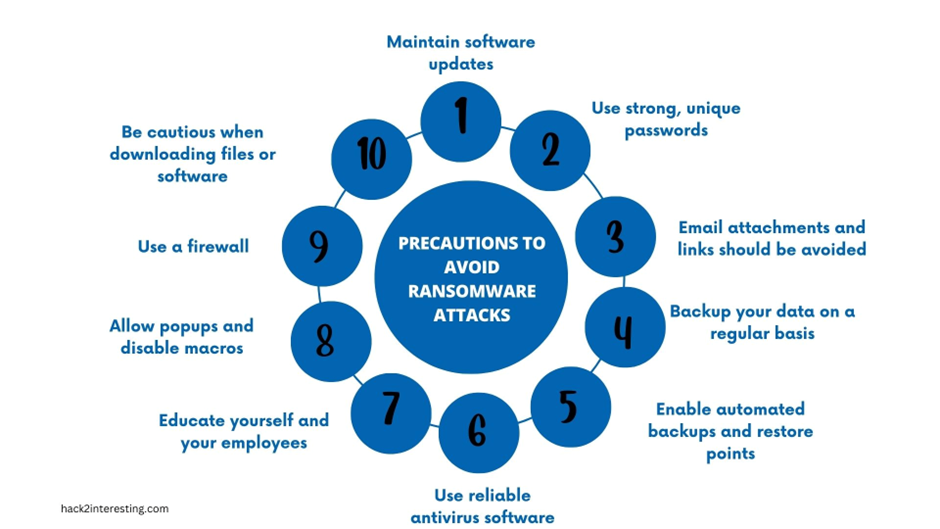
By following these guidelines, you may dramatically lower your chances of becoming a victim of a ransomware attack and protecting your data and devices.
Some of the best security software alternatives for ransomware protection are:
- FireEye employs a combination of next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, email security, and threat intelligence. The FireEye Helix platform from the corporation also features a ransomware decryption service.
- Mandiant: provides ransomware protection services including as incident response, threat intelligence, and managed security services. The Mandiant Advantage platform from the company offers a ransomware protection module that assists organizations in detecting, responding to, and recovering from ransomware attacks.
- Cisco Talos: delivers threat intelligence and analysis services to assist enterprises in protecting themselves against ransomware. Talos Intelligence Sharing Initiative (TISI) allows businesses to share threat intelligence with one another in order to develop collective defenses against ransomware.
- SentinelOne: detects and blocks ransomware threats using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. The Singularity platform from the firm also has a ransomware rollback capability that can assist enterprises in recovering from ransomware assaults.
- Bitdefender Antivirus Plus: Bitdefender has consistently received good marks from independent testing labs for its real-world protection against ransomware and other threats.
- Malwarebytes Premium: Malwarebytes aggressively prevents aggressive ransomware from gaining control of machines and demanding ransom payments.
- Avast One: Avast One is an award-winning, free anti-ransomware program that protects devices running Windows, Android, Mac, and iOS.
- Norton 360 Antivirus: Norton is known for providing effective overall ransomware protection and is regarded as one of the finest on the market.
CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) provides materials and recommendations to help enterprises combat ransomware more effectively.
Overall, ransomware attacks can have severe financial and operational consequences for businesses. It is critical to implement preventive measures and response methods in order to mitigate the dangers connected with ransomware.
