Insights into Iranian Cyber Espionage: APT33 Targets Aerospace and Energy Sectors and has Ties to Destructive Malware
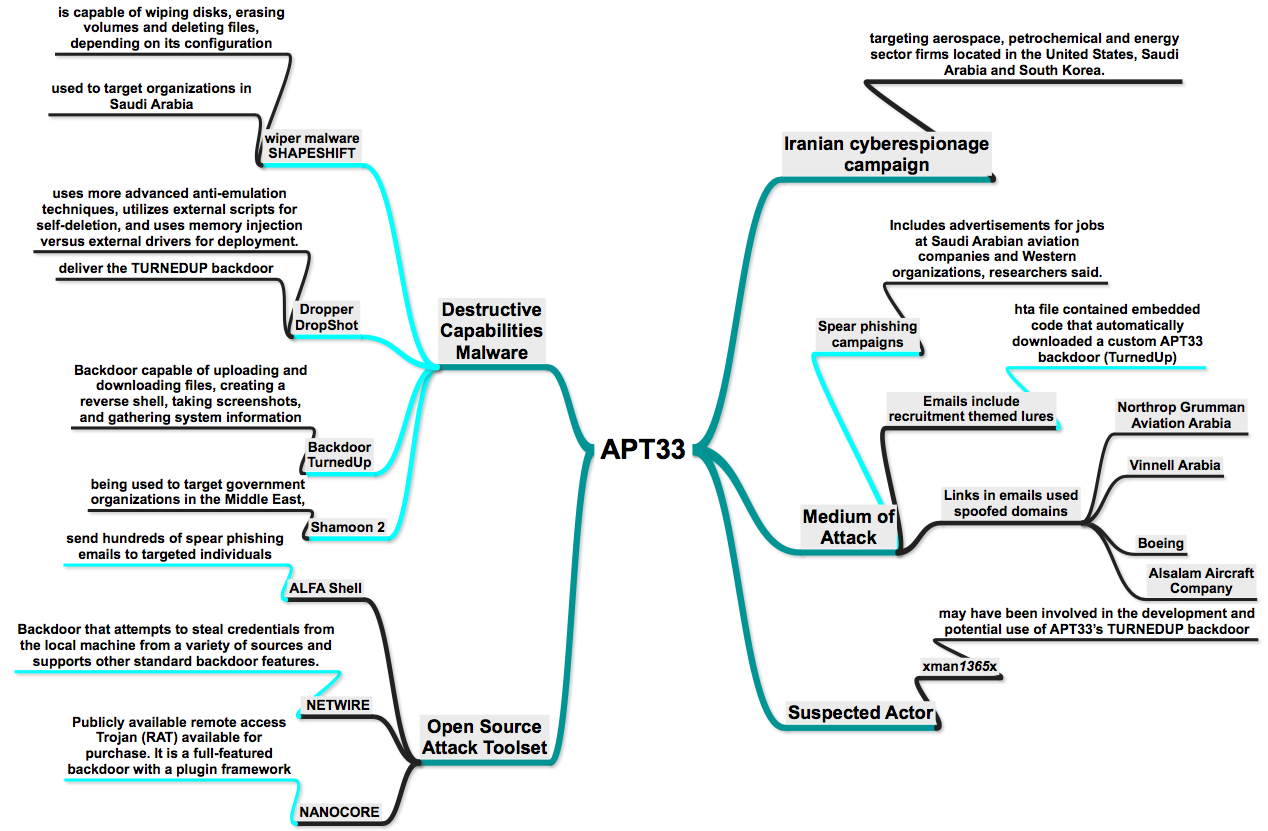
- APT33 is a capable group that has carried out cyber espionage operations since at least 2013
- APT33 has shown particular interest in organizations in the aviation sector involved in both military and commercial capacities, as well as organizations in the energy sector with ties to petrochemical production.
- From mid-2016 through early 2017, APT33 compromised a U.S. organization in the aerospace sector and targeted a business conglomerate located in Saudi Arabia with aviation holdings.
- APT33 may have targeted these organizations as a result of Iran’s desire to expand its own petrochemical production and improve its competitiveness within the region.
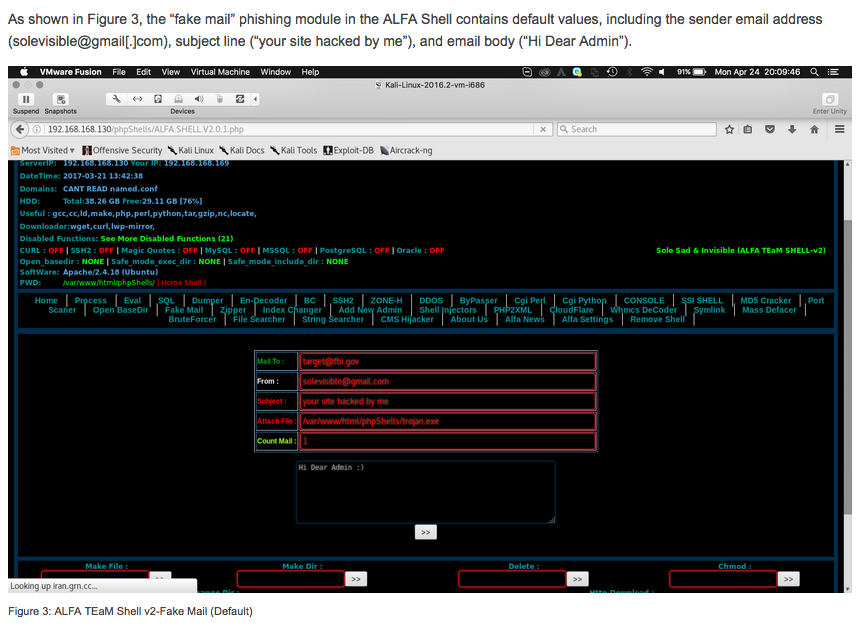
- APT33 leverages popular Iranian hacker tools and DNS servers used by other suspected Iranian threat groups. The publicly available backdoors and tools utilized by APT33 – including NANOCORE, NETWIRE, and ALFA Shell – are all available on Iranian hacking websites, associated with Iranian hackers, and used by other suspected Iranian threat groups
- The ties to SHAPESHIFT may suggest that APT33 engages in destructive operations or that they share tools or a developer with another Iran-based threat group that conducts destructive operations.
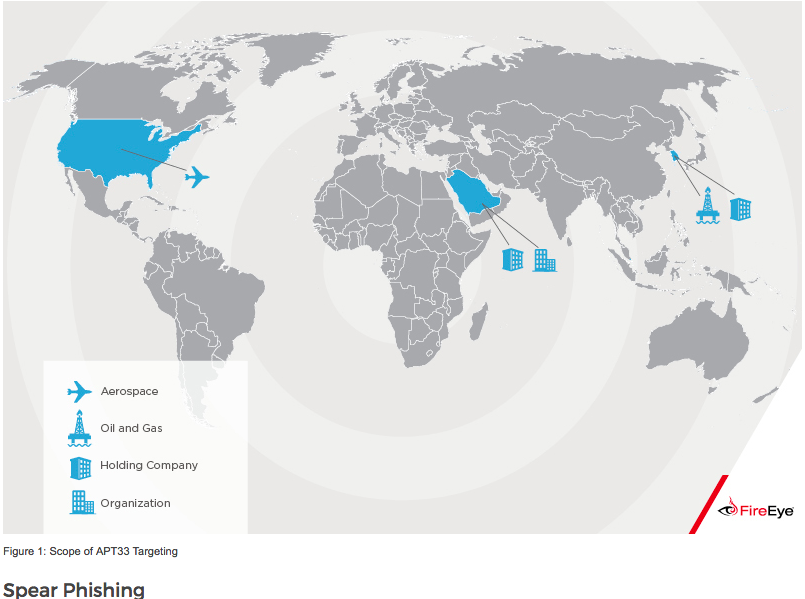
Targetted/Affected Organizations
APT33 has shown particular interest in organizations in the aviation sector involved in both military and commercial capacities, as well as organizations in the energy sector with ties to petrochemical production.
- United States – Compromised a U.S. organization in the aerospace sector
- Saudi Arabia – A business conglomerate located in Saudi Arabia with aviation holdings.
- South Korea – Company involved in oil refining and petrochemicals
Suspects Analysis as per Media Coverage
Source : Iranian Cyber News Agency – Iranians Behind StoneDrill and NewsBeef Malware
- Mahdi Honarvar xman_1365_x is self-identified on forums as Mahdi Honarvar from Mashad. This is shown to be linked to the third wave of attacks by the Shamoon-2 wiper malware.Not being content with being exposed 3 years ago as a member of the Cyber Army Institute of Nasr, he has continued to work for the Kavosh front company, and this now shows that he and others, through their poor security procedures, have enabled others to easily link the malware back to the Iranian State, inviting retribution from those who were affected.
- The size of the NewsBeef and StoneDrill attacks suggests an organized team effort. Searches have revealed he could be part of an organized group. Some of those that Iran Khabarestan exposed were researching and developing spyware against conscientious and political opponents of the Islamic Republic might also be involved? They are as follows:
- Malek Mohammadinezhad – He is head of the fake Kavosh company and uses the email address
- Behzad Shamsi Achachluei – Spyware and malware developer for smartphones, uses the email address
- Saeid Beiki – Beiki discovers vulnerabilities and informs the IRGC so that they can spy on people and start cyberwars. His own resume states that in the past he has been a ‘Malware Analyst, Kavosh Security Center, Tehran’
- Mehdi Hoseinzadeh – Hoseinzadeh is a spyware developer.
- Milad Torkashvan – Torkashvan is involved with research and development -R&D- of cloud-based attack systems, working as a malware developer.
- Sayyed Javad Sayyedhamzeh – Sayyedhamzeh is a spyware and destructive malware developer.
- Javad Heidariyan – Heidariyan codes malware to spy on Iranians.
- Nima Nikju – Nikju -Nikjoo- works on coding malware to spy on Iranians.
- Mohammad Paryar – Paryar also codes malware to spy on Iranians.
- The original blogpost where this information is listed is from is on Iran Khabarestan available HERE. Two of those indicted by the USA FBI in 2016, Hamid Firuzi and Nader Saedi are also named in the article.
Malware Impacts
- The hackers remained inside of the systems of those affected for “four to six months” at a time, able to steal data and leaving behind the malware that FireEye refers to as Shapeshifter.
- Security firm Kaspersky first spotted ShapeShift in March of this year, calling it StoneDrill. Kaspersky noted that it resembles Shamoon, but with more techniques designed to evade security mechanisms, like the “sandbox” protections that limit a given application’s access to the rest of a target computer. Kaspersky wrote at the time that one of the two targets in which it found StoneDrill malware was European, whereas Shamoon’s attacks had been confined to the Middle East. “Why is this worrying?” asked Kaspersky founder Eugene Kaspersky in a blog post about the discovery. “Because this finding indicates that certain malicious actors armed with devastating cyber-tools are testing the water in regions in which previously actors of this type were rarely interested.”
- 7 March 2017 – Wiper also appears to be connected with NewsBeef, an advanced, persistent threat (APT) actor known for targeting Saudi Arabia by using the Browser Exploitation Framework known as BEeF.
- Kaspersky Labs also discovered a StoneDrill backdoor used for spying purposes, alongside four command-and-control (C&C) panels used to run and monitor destructive campaigns.
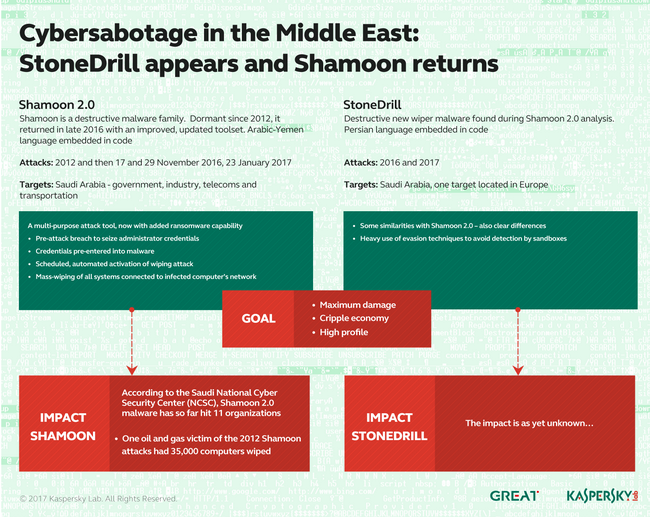
- ln 2016 another round of Shamoon attacks ripped through the Middle East, destroying thousands more machines, this time overwriting the drives with the image of the body of a 3-year-old Syrian refugee who drowned in the Mediterranean.
- the “Dark Seoul Gang” used wiper malware to destroy computer hard drives at South Korean banks and broadcasting facilities, as well as attack the country’s financial companies.- zdnet
- In 2012, Iran-linked hackers calling themselves “Cutting Sword of Justice” used a piece of similar “wiper” malware known as Shamoon to overwrite the hard drives of 30,000 computers at Saudi oil behemoth Saudi Aramco and Qatari natural gas producer RasGas with the image of a burning US flag.
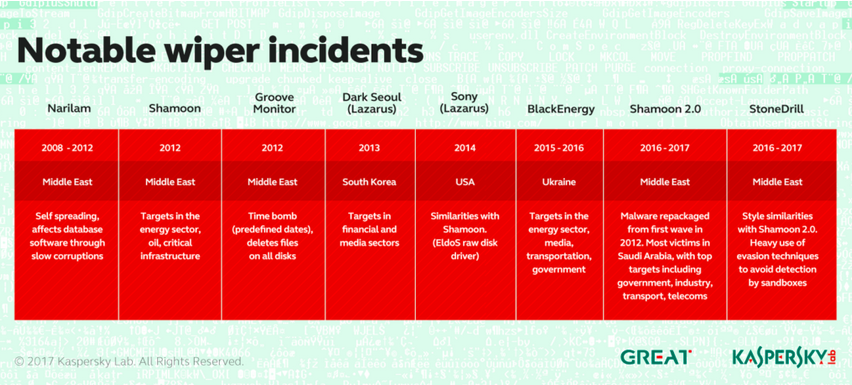
Source :- eugene.kaspersky.com StoneDrill: We’ve Found New Powerful ‘Shamoon-ish’ Wiper Malware – and It’s Serious.
Research Reports and Analysis
- 1 September 2012 – Shamoon The Wiper – Kaspersky Lab Analysis
- 27 April 2016 – wiper also appears to be connected with NewsBeef, an advanced, persistent threat (APT) actor known for targeting Saudi Arabia by using the Browser Exploitation Framework known as BEeF.- Kaspersky Lab Analysis
- 30 – FireEye Responds to Wave of Destructive Cyber Attacks in Gulf Region – Shamoon 2.0 Analysis by Fireeye Team
- 7 March 2016 – FROM SHAMOON TO STONEDRILL Wipers attacking Saudi organizations and beyond – Kaspersky Lab Analysis Report
- – APT33 Targets Aerospace and Energy Sectors and has Ties to Destructive Malware – APT33 Analysis by Fireeye Team
Threat Intelligence and Prevention Advisories
- 4 July 2017 Remove Trojan StoneDrill
- 22 August 2017 Virustotal Analysis
- 15 Microsoft Windows Defender Security Intelligence – Trojan:Win32/WipMBR.B is a trojan that overwrites your computer’s MBR (master boot record) and other files, thus preventing you from accessing your operating system and using your computer
Media Coverage
- Insights into Iranian Cyber Espionage: APT33 Targets Aerospace and Energy Sectors and has Ties to Destructive Malware – Fireeye Report
- The Iran-linked APT33 group has been targeting aerospace and energy organizations in the United States, Saudi Arabia, and South Korea.- Securityaffairs
- Suspected Iranian Hackers Targeted U.S. Aerospace Sector – Thedailybeast
- Security experts: Iran-backed hackers targeting U.S. and Saudi Arabia – CNN Tech
- APT33: Researchers Expose Iranian Hacking Group Linked to Destructive Malware – thehackernews
- 8 March 2017 – StoneDrill advanced wiper malware discovered in the wild – scmagazine
- 8 March 2017 – StoneDrill A New Rising Malware to Wipe Disks – cyberwhizz
- 7 March 2017 – Shamoon malware spawns even nastier ‘StoneDrill’ – Data-destroying code moves on from Middle East, now rampaging through Europe – theregister
- 6 March 2017 – From Shamoon to StoneDrill Wipers attacking Saudi organizations and beyond – Kaspersky Lab
- 6 Marrch 2017 – Destructive StoneDrill Wiper Malware On The Loose – threatpost