May 2024-Cybersecurity Trends: Ransomware, Nation-State Attacks, Zero-Day Exploits. Get your monthly roundup of the most critical security vulnerabilities and emerging threats.
1. Week-01-May-2024 : 1st May 2024 till 5th May 2024
Ransomware:
Victim sector – Government
Date– 5th May 2024
Victim- City of Wichita, US
Attack – Hackers infiltrated the city’s computer network and deployed ransomware that encrypted critical systems. This means the data became inaccessible unless a ransom was paid.
Impact: The attack forced the city to shut down many online services, disrupting things like:
- Online bill payments for utilities and municipal courts
- Public transportation fare collection
- Public Wi-Fi at the airport and libraries
- First responders are switching to backup procedures.
Reference: https://www.wichita.gov/1199/Alert
Impacted Divisions by Ransomware Attack:
- External vendor systems: Park & Recreation’s summer programming
- Park & Recreation Department: Online registration for summer activities is back up and running
- Golf Wichita: Now able to accept credit card payments both in our clubhouses and through our online store
Current Status: As of today, June 1st, 2024, the situation is ongoing. The city is still working on restoring systems and hasn’t announced a timeline for full recovery.
2. Week-02-May-2024 : 6th May 2024 till 12th May 2024
Ransomware
#StopRansomware: Black Basta
On May 10th, 2024, a joint Cybersecurity Advisory (#StopRansomware: Black Basta) was issued by CISA, FBI, HHS, and MS-ISAC.
Target: This advisory specifically focused on Black Basta, a ransomware variant known for its severity. Black Basta attacks critical infrastructure sectors like healthcare and steals data before encryption, making them a high-value target for attackers.
Goal: The primary aim was to equip defenders with the knowledge and resources needed to identify and effectively defend against Black Basta attacks.
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa24-131a
3. Week-03-May-2024 : 13th May 2024 till 19th May 2024
Ransomware
Victim sector– Healthcare
Date– 17th May 2024
Victim– MediSecure
- Australians’ prescription records breached in large-scale ransomware attack
- A MediSecure database containing the personal and limited health information of individuals relating to prescriptions, as well as healthcare provider information has been affected by this cyber security incident.
Attack: The attack involved ransomware, a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands a ransom payment for decryption.
Impact: The attack compromised the personal and health information of individuals, including:
- Basic personal details
- Prescription information (limited)
- Information on healthcare providers
Data Leak: As of today, June 2nd, 2024, there haven’t been any reports of leaked data online. However, the investigation is ongoing.
Disruption: MediSecure mitigated the attack and reported no ongoing issues accessing medication.
Incident Update: https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7197044836380626944/
Critical Vulnerabilities POC
Mura/Masa CMS – CVE-2024-32640
A recently discovered SQL injection vulnerability called CVE-2024-32640 affects the open-source enterprise content management system Mura/Masa CMS. Should the vulnerability be effectively exploited, it might grant unauthorized attackers access to confidential information.
Reference: 1. https://github.com/Stuub/CVE-2024-32640-SQLI-MuraCMS
2. https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-99835
Nation-State Attacks
North Korean Hacker Group – Kimsuki
A new strain of Linux malware known as Gomir, which is a trojanized software installer-delivered backdoor version of GoBear, has been employed by the North Korean hacker group Kimsuki.
Kimsuky is a state-sponsored threat actor associated with the Reconnaissance General Bureau (RGB), North Korea’s military intelligence organization.
Malware:
- Gomir Backdoor
- GoBear
- Troll Stealer
Targeted Countries: South Korea
Targeted Industries:
- Public sector
- Government agencies
- construction
Impact – Device compromise:
1. Espionage
2. Data theft
Critical Vulnerabilities to Patch
- The Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog is maintained by CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) as a resource for network defenders and the cybersecurity community at large
- It serves as a central repository of vulnerabilities that are confirmed to be actively exploited by malicious actors
Reference: https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories
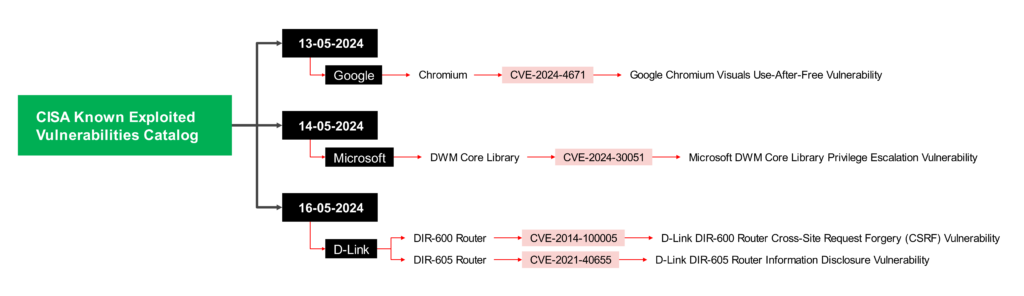
1. 13-05-2024: Chromium- CVE-2024-4671
CVE-2024-4671 is indeed a critical vulnerability that affected Chromium browsers like Google Chrome
- Description: CVE-2024-4671 was a “use after free” vulnerability in Chromium’s Visuals component. This type of vulnerability occurs when a program continues to use a memory location after it’s been freed, potentially allowing attackers to manipulate data or crash the program.
- Impact: A remote attacker who could exploit this vulnerability had the potential to perform a sandbox escape.
- Patch: Google released a security update to address CVE-2024-4671 on Patch Tuesday, May 14th, 2024. This update patched the vulnerability and mitigated the risk of exploitation.
- Update: https://x.com/CISACyber/status/1790035634884681990
2. 14-05-2024: Microsoft- CVE-2024-30051
CVE-2024-30051 is a critical vulnerability in Microsoft’s DWM Core Library, a core component responsible for managing the Desktop Window Manager (DWM) on Windows systems.
Impact:
- This vulnerability is classified as critical because it allows an attacker with low privileges to potentially escalate their privileges to the administrator level. This means an attacker could gain complete control over a vulnerable system.
- Attackers could exploit this vulnerability to install malware, steal sensitive data, or disrupt critical system functions.
3. 16-05-2024: D-Link
- DIR-600 Router: CVE-2014-100005
This vulnerability is a serious issue because it allows a remote attacker to hijack an administrator’s session and perform malicious actions on the router. - DIR-605 Router: CVE-2021-40655
This vulnerability is from 2021 and allows attackers to steal a router’s username and password through a forged request.
Zero-Days Exploited in the Wild
CVE-2024-4671
CVE-2024-4671 was a serious vulnerability in the Google Chrome browser that emerged in May 2024
- Type: Use-after-free vulnerability in the Visuals component
- Severity: Critical (CVSS score likely high)
- Impact: A Successful exploit could allow for arbitrary code execution in the context of the logged-on user.
Affected Products-Google Chrome before 124.0.6367.201/.202
Fixed Version-Google Chrome version 124.0.6367.201 or later - Reported by: Anonymous Researcher
4. Week-04-May-2024: 20th May 2024 till 26th May 2024 28
Ransomware
Victim sector-Government
Date-21st May 2024
Victim–Ikaruz Red Team | Hacktivist Group Leverages Ransomware for Attention Not Profit
- IRT is a known hacktivist group based in the Philippines.
- They are known for using ransomware and other disruptive tactics to draw attention to their political causes.
- Their targets are often Philippine government entities or corporations.
Targets: -Philippines government
-January and September of 2023 – multiple Philippine entities.
Tactics: They’ve been reported to use a variety of leaked ransomware builders, including:
- LockBit
- JellyFish
- Vice Society
- ALPHV
- BianLian
- 8base
- Clop
Groups Attribution –
- Ikaruz Red Team
- Turk Hack Team
- Anka Underground
- Robin Cyber Hood
- Philippine Exodus
- Cyber Operations Alliance
- Philippine Hacking University
Nation-State Attacks
1. Tiny BackDoor Goes Undetected – Suspected Turla leveraging MSBuild to Evade detection
Date: 20 MAY 2024
Attribution– Turla group from Russia
Reference:
- 1. https://cyble.com/blog/tiny-backdoor-goes-undetected-suspected-turla-leveraging-msbuild-to-evade-detection/
- 2. https://www.darkreading.com/cyberattacks-data-breaches/russia-turla-apt-msbuild-tinyturla-backdoor
- 3. https://x.com/k3yp0d/status/1788590090324754477
2. Cybercriminals Are Targeting Elections In India With Influence Campaigns
Date: 21 MAY 2024
Targets: Primary types of malicious typologies targeting election integrity fall into five distinct categories
- Election infrastructure
- Political parties, campaigns, and public officials
- Covert influence operations to assist or harm political organizations, campaigns, or public officials
- Covert influence operations to influence public opinion and sow division
- Covert efforts to influence policymakers and the public
Attribution: Multiple Hacker Groups-
- Anon Black Flag | Indonesia
- Anonymous Bangladesh
- Morocco Black Cyber Army
- Toxcar Cyber Team
- Islamic Cyber Team
- Lulzsec Indonesia
- TEAM CYBER MAFIA
- ANON TEN BD
- Ketapang Grey Hat Team
- ANON SEC BD
- Team Ahadun Ahad (2.0)
- Bangladesh Dark Net
- Nixon Cyber Team
- Cyber Sheild Force BD
- UnitedSec-313
- Sylhet Gang
3. Invisible miners: unveiling GHOSTENGINE’s crypto mining operations
Date: 22 MAY 2024
Targets: known EDR agents
- scans and compares all the running processes with a hardcoded list of known EDR agents
- terminates any active EDR agent processes
Method:
1. Avast Anti-Rootkit Driver file
2. IObit
Reference: https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/invisible-miners-unveiling-ghostengine
4. Operation Diplomatic SpecterAn Active Chinese Cyberespionage Campaign Leverages Rare Tool Set to Target Governmental Entities in the Middle East, Africa and Asia
Date: 24th May 2024
Targets: Government organizations in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. This includes ministries of foreign affairs, military entities, embassies, and more.
- Embassies
- Military operations
- Political meetings
- Ministries of the targeted countries
- High-ranking officials
- Diplomatic and economic missions
Attribution: Chinese state-aligned
Impact:
- Embassies’ email boxes targeted by the threat actor.
- Events encompass a wide range of subjects
- Military operations
- Meetings
- Summits
- Conflicts
- Other pertinent aspects of current geopolitical affairs
5. Week-05-May-2024 : 27th May 2024 till 31st May 2024
Critical Vulnerabilities to Patch in May 2024
1. CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
It serves as a central repository of vulnerabilities that are confirmed to be actively exploited by malicious actors
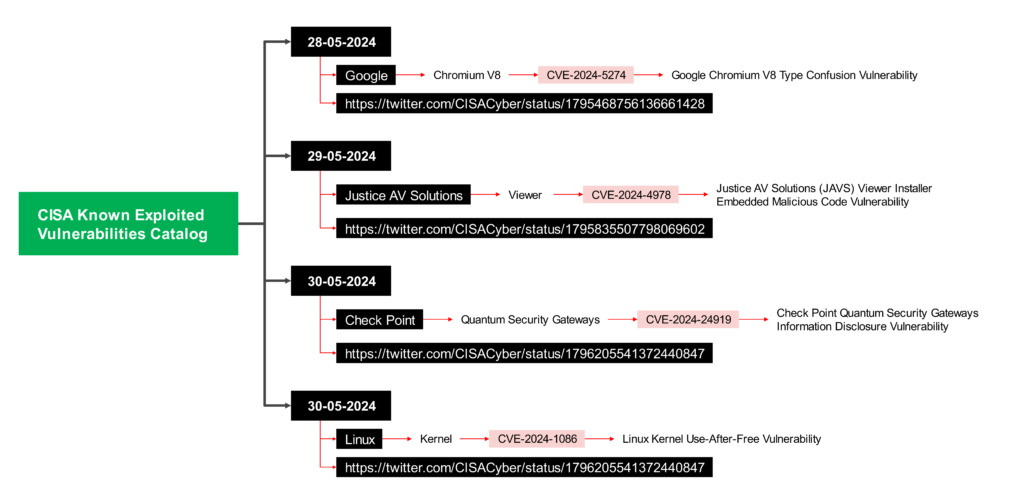
- 28-05-2024 : Google: CVE-2024-5274
CVE-2024-5274 appears to be a critical vulnerability in Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine identified in May 2024.
Type: Likely a use-after-free vulnerability in V8. Use-after-free vulnerabilities occur when a program tries to access memory that has already been freed, potentially leading to program crashes or attackers injecting malicious code.
Impact: Attackers could potentially steal data, install malware, disrupt critical operations, or take complete control of the system.
Reference: https://twitter.com/CISACyber/status/1795468756136661428 - 29-05-2024: Justice AV Solutions: CVE-2024-4978
CVE-2024-4978 is a critical vulnerability affecting the Justice AV Solutions (JAVS) Viewer software, specifically version 8.3.7.250-1
Type: Embedding Malicious Code – The JAVS Viewer installer itself contained malicious code.
Impact: A remote attacker with low privileges could potentially exploit this vulnerability to execute unauthorized PowerShell commands on a vulnerable system. This could allow attackers to:- Install malware
- Steal sensitive data
- Disrupt critical system functions
- 30-05-2024: Check Point: CVE-2024-24919
CVE-2024-24919- Check Point Quantum Security Gateways contain an unspecified information disclosure vulnerability.
This vulnerability affected Check Point Security Gateways with either the IPsec VPN or Mobile Access software blade enabled, specifically when included in the Remote Access VPN community.
Reference: https://twitter.com/CISACyber/status/1796205541372440847 - 30-05-2024: Linux: CVE-2024-1086
Type: Use-after-free vulnerability in the netfilter: nf_tables component
Affected Systems: This vulnerability affects Linux systems running kernels between versions 5.14 and 6.6, including popular distributions like Debian and Ubuntu.
Reference: https://twitter.com/CISACyber/status/1796205541372440847
POC released in the wild
Fortinet FortiSIEM
1. CVE-2024-23108
Base Score-9.8 CRITICAL
- CVE-2024-23108 was a critical vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiSIEM product
- It allowed remote attackers to execute malicious code on vulnerable systems without any authentication required.
Reference: https://github.com/horizon3ai/CVE-2024-23108
2. CVE-2023-34992
Base Score9.8 CRITICAL
This vulnerability is classified as critical because it grants attackers the ability to remotely execute code on vulnerable systems.pen_spark
Reference: https://github.com/horizon3ai/CVE-2023-34992
Zero-Days Exploited in the wild
CVE-2024-24919 – Quantum Gateway Information Disclosure
Base Score: 8.6 HIGH
Potentially allowing an attacker to read certain information on Check Point Security Gateways once connected to the internet and enabled with remote Access VPN or Mobile Access Software Blades. A Security fix that mitigates this vulnerability is available.
Reference: https://support.checkpoint.com/results/sk/sk182336
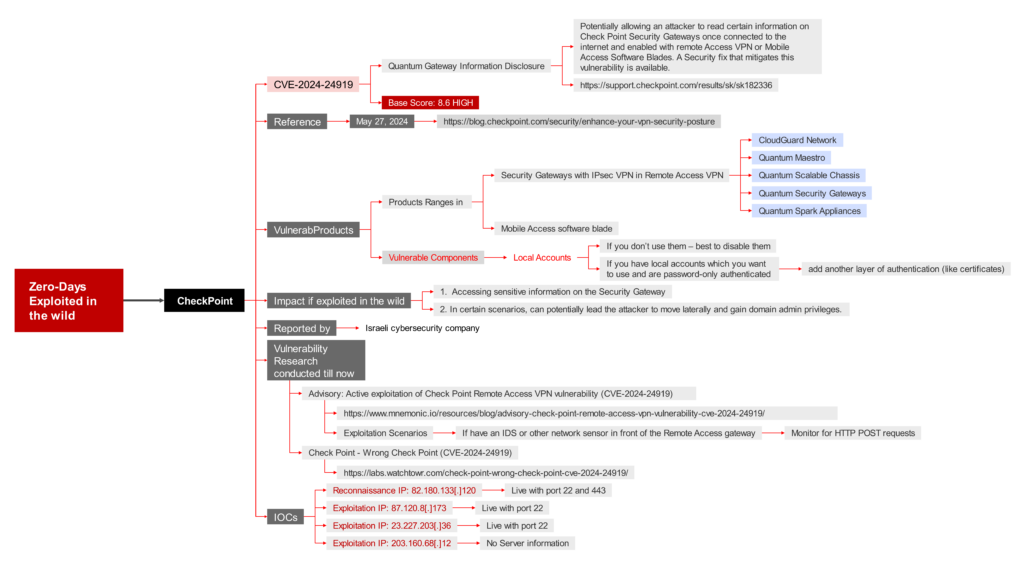
Impact if exploited in the wild
- Accessing sensitive information on the Security Gateway
- In certain scenarios, can potentially lead the attacker to move laterally and gain domain admin privileges.
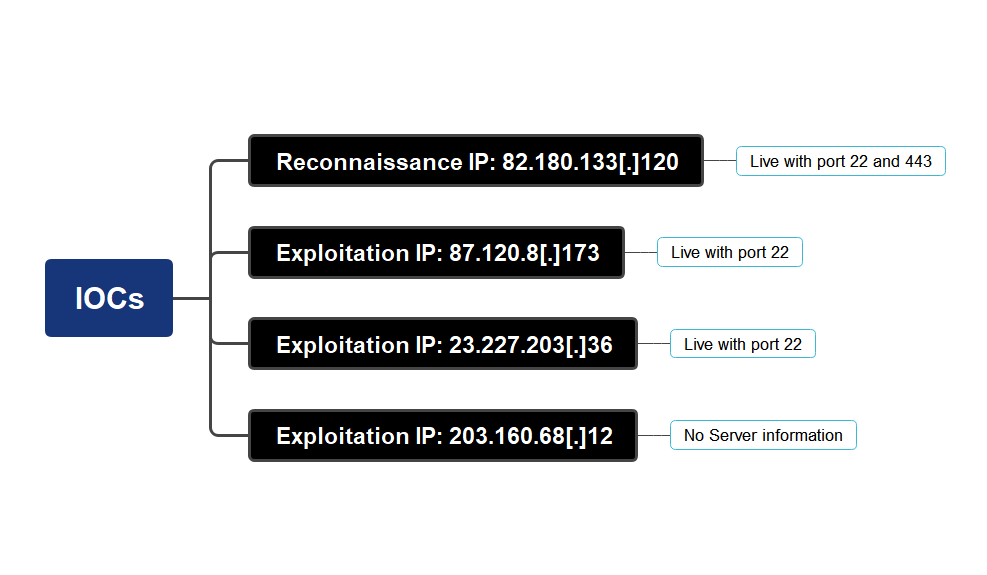
IOCs
List of Zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in the wild for Chrome till now:
CVE-2024-0519
A high-severity out-of-bounds memory access weakness within the Chrome V8 JavaScript engine, allows remote attackers to exploit heap corruption via a specially crafted HTML page, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive information.
CVE-2024-2887
A high-severity type confusion flaw in the WebAssembly (Wasm) standard. It could lead to remote code execution (RCE) exploits leveraging a crafted HTML page.
CVE-2024-2886
A use-after-free vulnerability in the WebCodecs API used by web applications to encode and decode audio and video. Remote attackers exploited it to perform arbitrary reads and writes via crafted HTML pages, leading to remote code execution.
CVE-2024-3159
A high-severity vulnerability caused by an out-of-bounds read in the Chrome V8 JavaScript engine. Remote attackers exploited this flaw using specially crafted HTML pages to access data beyond the allocated memory buffer, resulting in heap corruption that could be leveraged to extract sensitive information.
