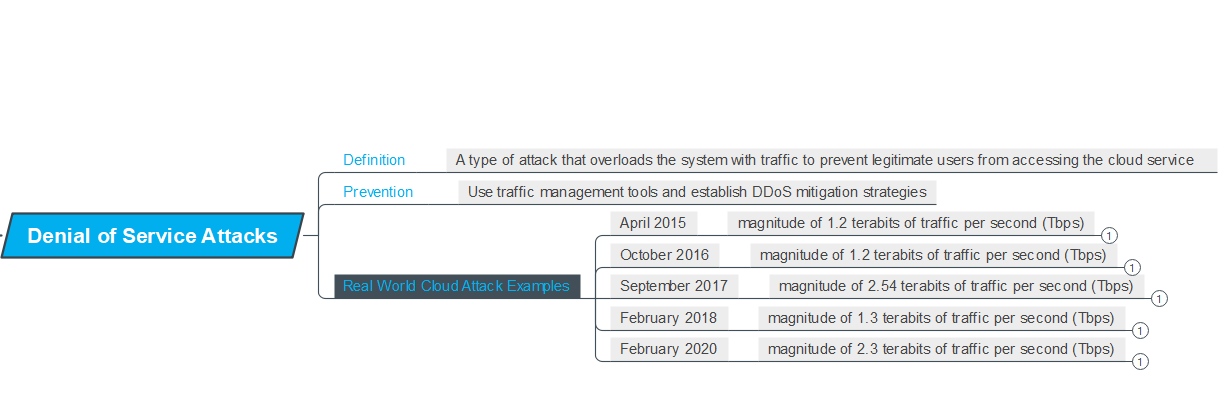
Definition
A type of attack that overloads the system with traffic to prevent legitimate users from accessing the cloud service
Prevention
Use traffic management tools and establish DDoS mitigation strategies
Real World Cloud Attack Examples
April 2015
magnitude of 1.2 terabits of traffic per second (TBps)
1.Two technical investigations claim that hackers who have access to China’s Internet backbone are responsible for the enormous denial-of-service attacks that have occasionally prevented GitHub from operating
2.for more than five days. As previously reported, millions of computer users both inside and outside of China continuously load and reload the two GitHub pages, creating an infinite loop that caused unabated outages across the whole GitHub network as well as the two targeted pages. Every computer that is attacking the GitHub servers is running malicious code that secretly enlists it as a soldier in a vast DDoS army. https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2015/03/massive-denial-of-service-attack-on-github-tied-to-chinese-government/
October 2016
magnitude of 1.2 terabits of traffic per second (TBps)
A significant percentage of the domain name system (DNS) infrastructure on the internet is managed by the servers of Dyn, a company. This devastating attack caused downtime on a number of significant websites, including Airbnb, Netflix, PayPal, Visa, Amazon, The New York Times, Reddit, and GitHub. According to Dyn, “100,000 malicious endpoints” linked to the Mirai Botnet were employed in the attack.
September 2017
magnitude of 2.54 terabits of traffic per second (TBps)
2017’s September saw the largest DDoS assault to date. Having a magnitude of 2.54 TBps, the attack concentrated on Google services. In October 2020, Google Cloud announced the hack.
February 2018
magnitude of 1.3 terabits of traffic per second (TBps)
One of the biggest verifiable DDoS attacks on record targeted GitHub, a well-known website for managing source code that is used by millions of developers. 126.9 million packets were sent per second during this attack, which had a throughput of 1.3 TBps. The GitHub DDoS assault was a memcached DDoS assault, hence no botnets were involved. As an alternative, the attackers made use of memcached, a well-known database caching technique, and its amplifying impact.
February 2020
magnitude of 2.3 terabits of traffic per second (TBps)
In February 2020, AWS announced that it had stopped a significant DDoS attack. This attack generated 2.3 terabits of traffic per second (TBps) at its height. Which customer was the target of the attack? AWS wouldn’t say.